Adult Corn Rootworm Management
October 11, 2023
Adult Corn Rootworm Beetle Scouting and Management
- Controlling adult corn rootworm beetles to protect silking ears is not the same as controlling these beetles to suppress future larval populations.
- Adult control intended to prevent larval injury to plants the following season must be well timed to be effective.
- Tank mixing an insecticide with the fungicide applied at tasseling is often unsuited for adult corn rootworm beetle control.
The Importance of Scouting for and Managing Corn Rootworm (CRW) Adults
Scouting for corn rootworm (CRW) adults may benefit growers in several ways by helping growers reduce input costs and lower the risk of economic loss from CRW. If timed correctly, the combination of scouting and the application of control tactics that suppress CRW adults may reduce egg, potentially reducing the overall larval population the following year and protecting the current season yield potential in situations where significant silk clipping may occur.
Adult Identification
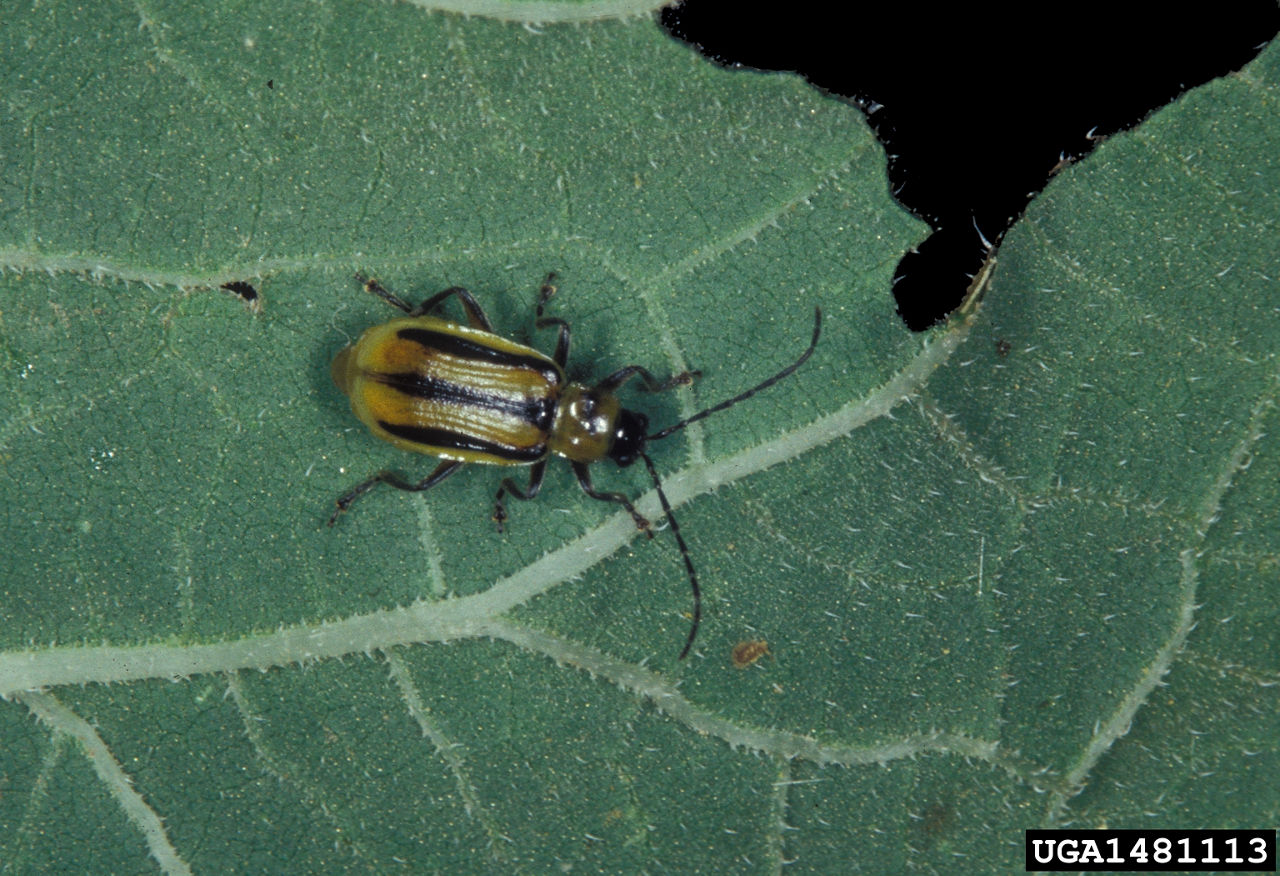
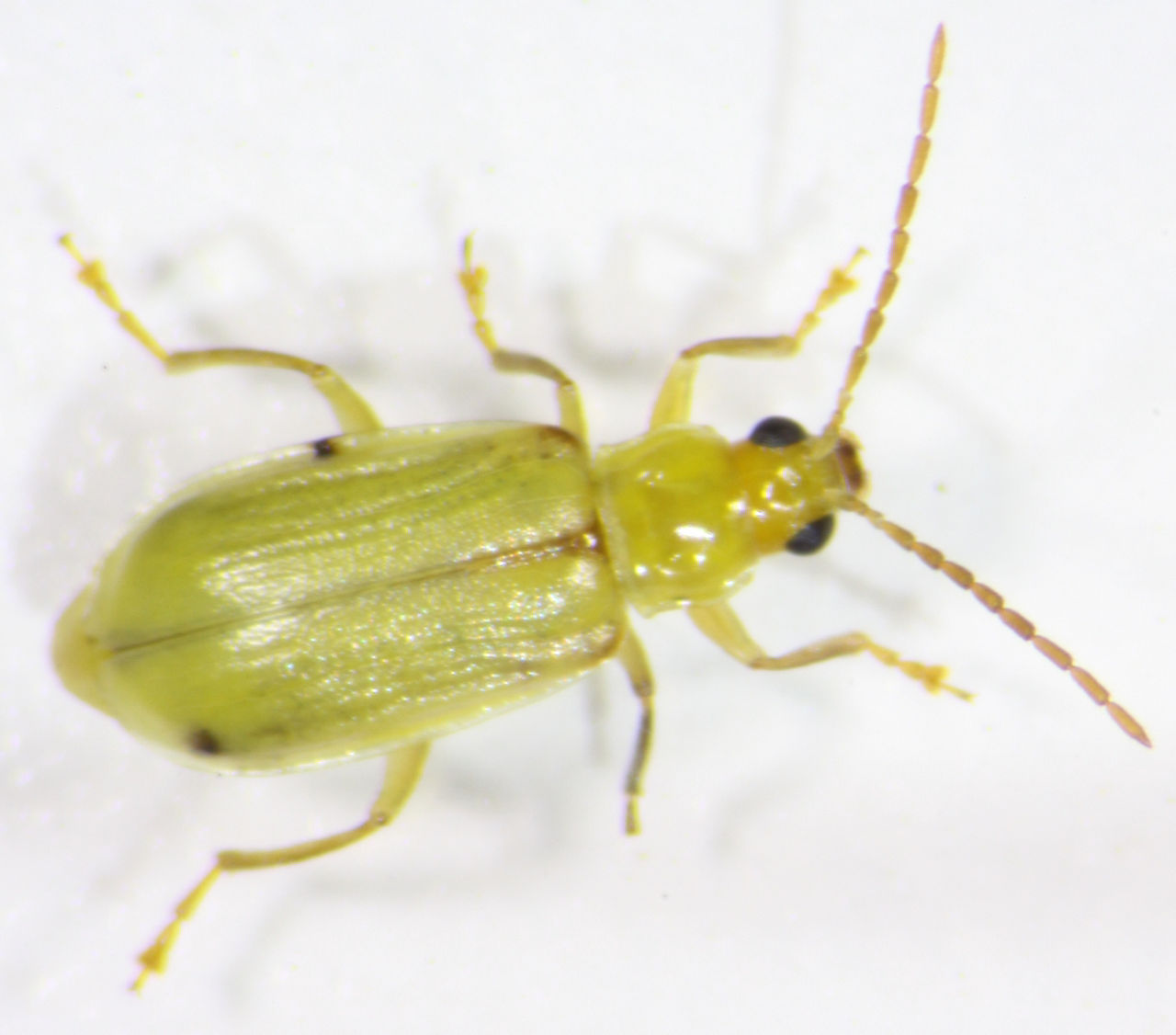
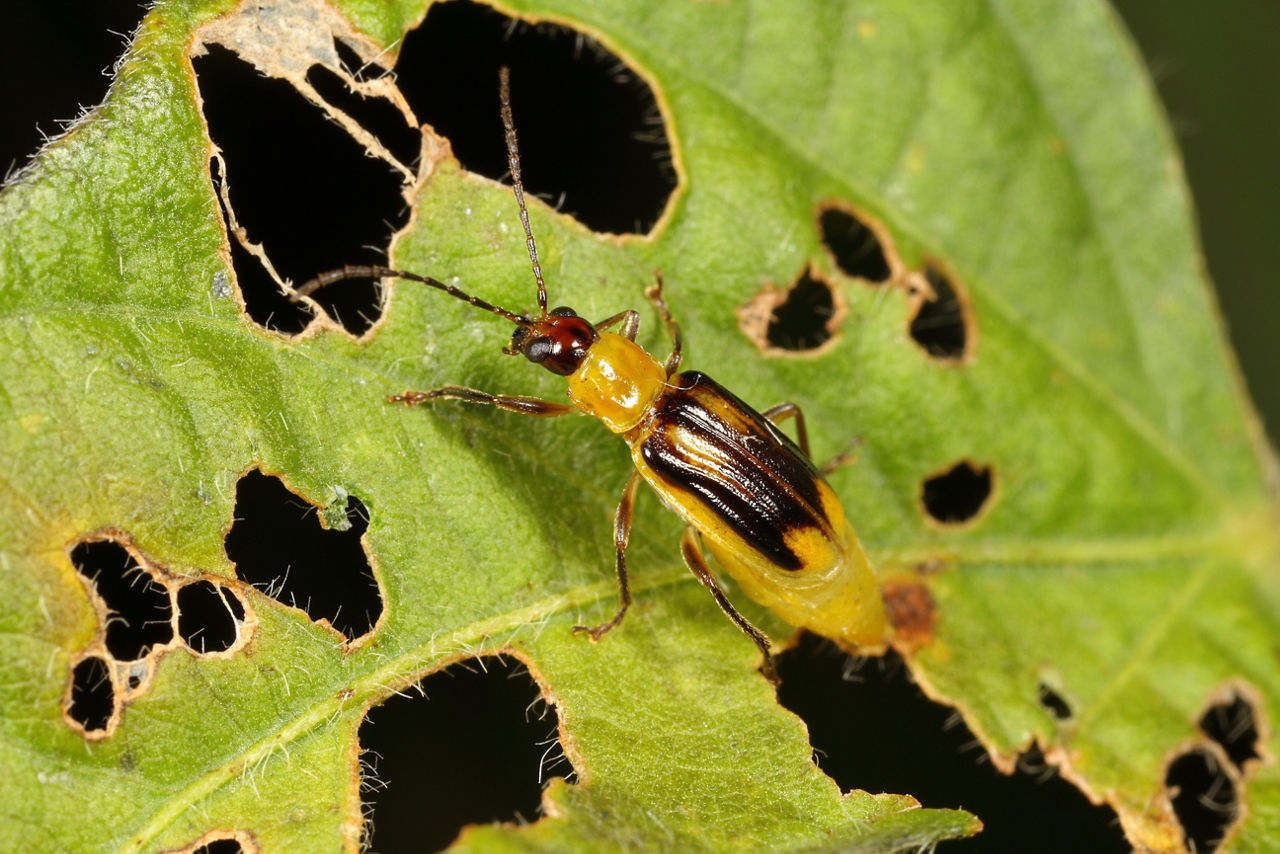
Two CRW species, the western corn rootworm and the northern corn rootworm, account for the majority of CRW injury in the Corn Belt. While the larvae of both species are very similar and can be difficult to distinguish from one another, the adults—while similar in size—are very different in appearance. The wing covers of the Western corn rootworm (WCR) adult are yellow with black stripes (Figure 1) or can be completely black (Figure 2). The northern corn rootworm (NCR) adults are yellowish green to green, with females being slightly longer and having larger abdomens (Figure 3).