The Effect of Tillage Practice on Corn and Soybean Yield Potential
June 21, 2022
TRIAL OBJECTIVE
Reduced tillage has many advantages in crop production systems. Crop residue on the soil surface can reduce erosion and conserve soil moisture. Additionally, minimizing soil disturbance contributes to better soil health. However, questions arise concerning how tillage practices could affect crop yield potential.
The objectives of this study were to demonstrate differences between tillage practices and to evaluate the effect of reduced fertilizer rates under strip tillage.
RESEARCH SITE DETAILS
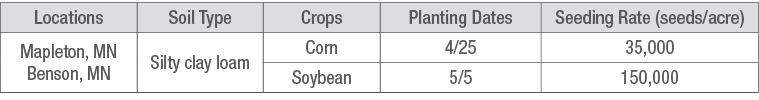
The study design was a randomized complete block with either 1 replication (Benson, MN) or 2 replications (Mapleton, MN) with five treatments (Table 1) over 3 years: 2019, 2020, and 2021.
Rainfed system under a corn-soybean rotation.
Strip-till treatments were established using a KUHN Krause Gladiator® 1205M strip-till machine with a Montag® Gen II fertilizer system.
Fertilizer was surface-applied in the fall to the Conventional and No-till treatments and incorporated or left on the surface, respectively.
The Strip-till treatment was completed in the fall and planted directly in the spring (Figure 1).
All corn plots received a total nitrogen application of 160 lb/acre.
Potassium and phosphorus fertilizer application rates were based on removal from the previous crop.
Weeds were controlled uniformly across the study area.
Plots were combine-harvested with grain moisture content, test weight, and total weight collected.
Statistical analysis for Fisher’s LSD was performed.
Table 1. Experiment treatments.
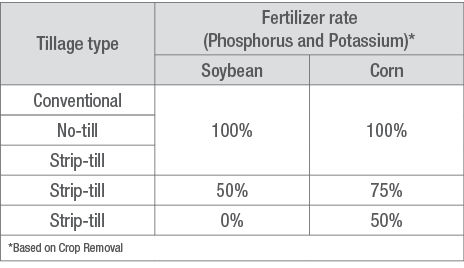
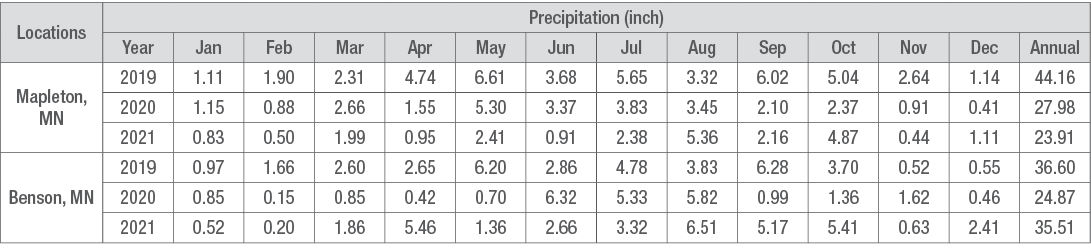
Table 2. Monthly and annual precipitation data for Mapleton, MN and Benson, MN.

UNDERSTANDING THE RESULTS
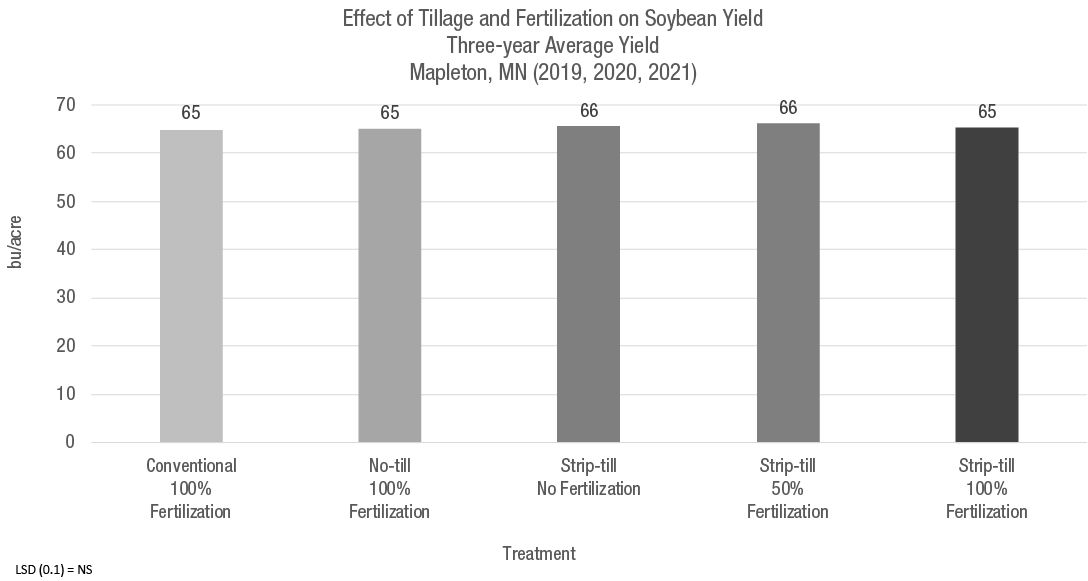
Mapleton, MN
Corn and soybean yield, three-year average.
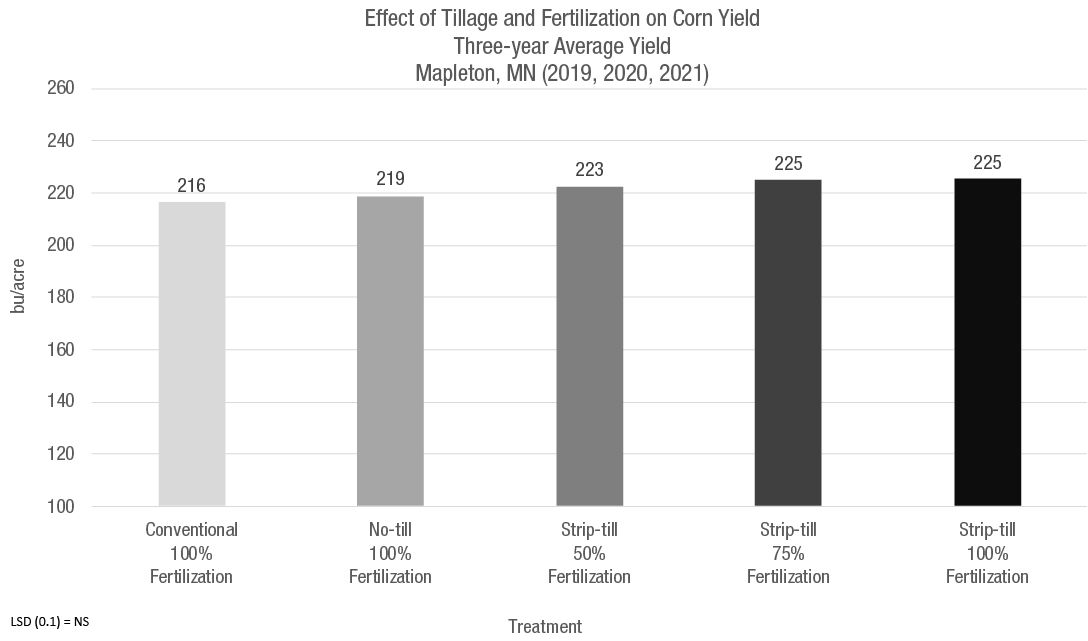
The highest three-year average corn yields were obtained under strip-till followed by no-till regardless of fertilization (Figure 2). However, the yield difference was not statistically significant.
For corn, conventional tillage tended to yield less than no-till and strip-till (Figure 2).
There was no difference in average soybean yield between treatments at this site, even with different fertilization management (Figure 3).
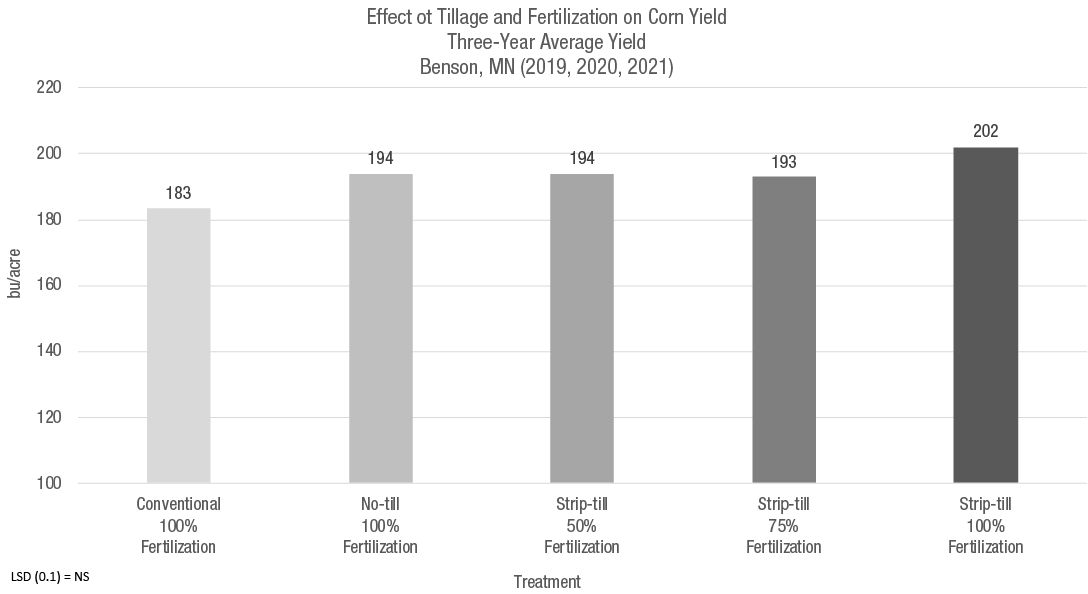
Benson, MN
Corn and soybean yield, three-year average.
Although not significant, strip-till plots with the 100% fertilization rate had the highest three-year average corn yield, followed by the rest of Strip-till and No-till treatments (Figure 4).
Conventional tillage yielded at least 10 bushels per acre less on average than the rest of treatments (Figure 4).
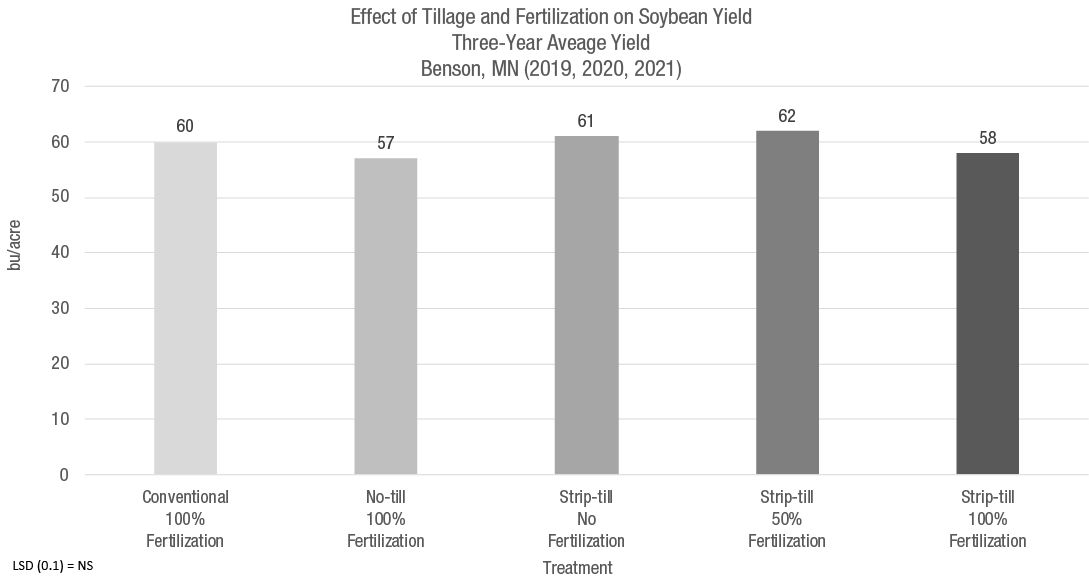
Like in Mapleton, there was no difference in average soybean yield between treatments at this site, even with different fertilization management (Figure 5).
KEY LEARNINGS
Strip-till and no-till tillage practices increased corn yield compared to conventional tillage at both locations. However, the differences were not statistically significant for the three-year averages.
For soybean, no clear tillage or fertilization effect was observed at both locations.
In general, reduced potassium and phosphorus fertilization under strip-till did not affect corn and soybean yield in these trials.
- Farmers should work with their local sales team member to help identify the best management practice for their production systems.
1117_26600
Seed Brands & Traits
Crop Protection
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
- always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices. to review additional important information, click to open the menu below.expand_more
No dicamba may be used in-crop with seed with Roundup Ready® Xtend Technology, unless and until approved or specifically permitted, and no dicamba formulations are currently registered for such use in the 2024 season. Please follow www.roundupreadyxtend.com/xtendimaxupdates for status updates
Based on Court ruling and EPA Existing Stocks Order* on XtendiMax® Herbicide registration, Bayer has stopped its sale and distribution of XtendiMax® Herbicide. Visit our XtendiMax herbicide updates page to learn the latest www.roundupreadyxtend.com/xtendimaxupdates.
*Low-volatility dicamba products subject to the ruling include XtendiMax® herbicide with VaporGrip® Technology, Engenia® herbicide and Tavium® Plus VaporGrip® Technology herbicide.
The Preceon™ Smart Corn System, including short stature corn developed through traditional breeding, is expected to be available, subject to final commercialization decisions, for planting in the 2024 growing season.
Short stature corn developed through biotechnology is not currently available for commercial sale or commercial planting. Commercialization is dependent on multiple factors, including successful conclusion of the regulatory process.
This material may contain “forward-looking statements” based on current assumptions and forecasts made by Bayer management. Various known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors could lead to material differences between the actual future results, financial situation, development or performance of the company and the estimates given here. These factors include those discussed in Bayer’s public reports which are available on the Bayer website at www.bayer.com. The company assumes no liability whatsoever to update these forward-looking statements or to conform them to future events or developments.
*Commercialization is dependent on multiple factors, including successful conclusion of the regulatory process. The information presented herein is provided for educational purposes only, and is not and shall not be construed as an offer to sell, or a recommendation to use, any unregistered pesticide for any purpose whatsoever. It is a violation of federal law to promote or offer to sell an unregistered pesticide.
Bayer is a member of Excellence Through Stewardship® (ETS). Bayer products are commercialized in accordance with ETS Product Launch Stewardship Guidance, and in compliance with Bayer’s Policy for Commercialization of Biotechnology-Derived Plant Products in Commodity Crops. Commercialized products have been approved for import into key export markets with functioning regulatory systems. Any crop or material produced from this product can only be exported to, or used, processed or sold in countries where all necessary regulatory approvals have been granted. It is a violation of national and international law to move material containing biotech traits across boundaries into nations where import is not permitted. Growers should talk to their grain handler or product purchaser to confirm their buying position for this product. Excellence Through Stewardship® is a registered trademark of Excellence Through Stewardship.
XtendiMax® herbicide with VaporGrip® Technology has been classified as pesticide and must be used with VaporGrip® Xtra Agent (or an equivalent volatility reduction adjuvant). For approved tank-mix products (including VRAs and DRAs), nozzles and other important label information visit XtendiMaxApplicationRequirements.com. Applicators must check XtendiMaxApplicationRequirements.com no more than 7 days before application of this product for additional labeling, including state restrictions. Where applicable, users must comply with additional requirements found on this website.
ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW PESTICIDE LABEL DIRECTIONS. Not all products are registered for use in all states and may be subject to use restrictions. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Check with your local dealer or representative for the product registration status in your state.
Product Use Statement: Enlist E3® soybeans contain the Enlist E3 trait that provides crop safety for use of labeled over-the-top applications of glyphosate, glufosinate and 2,4-D herbicides featuring Colex-D® technology when applied according to label directions. Following burndown, the only 2,4-D containing herbicide products that may be used with Enlist® crops are products that feature Colex-D technology and are expressly labeled for use on Enlist crops. 2,4-D products that do not contain Colex-D technology are not authorized for use in conjunction with Enlist E3 soybeans. Warning: Enlist E3 soybeans are tolerant of over-the top applications of glyphosate, glufosinate, and 2,4-D. Accidental application of incompatible herbicides to this variety could result in total crop loss. When using 2,4-D herbicides, grower agrees to only use 2,4-D products that contain Colex-D technology authorized for use in conjunction with Enlist E3 soybeans. Always read and follow herbicide label directions prior to use.
YOU MUST SIGN A TECHNOLOGY AGREEMENT, READ THE PRODUCT USE GUIDE PRIOR TO PLANTING AND FOLLOW HERBICIDE RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) REQUIREMENTS.
The transgenic soybean event in the Enlist E3® soybeans is jointly developed and owned by Corteva Agriscience and M.S. Technologies, L.L.C. ®™ Enlist, Enlist E3, the Enlist E3 logo and Colex-D are trademarks Corteva Agriscience and its affiliate companies.
Alloy™ and Connect™ are trademarks of M.S. Technologies, L.L.C., West Point, IA. Please read the M.S. Technologies, L.L.C. Use Restriction Agreement located at: - http://www.mstechseed.com/use-restriction-agreement/.
ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW PESTICIDE LABEL DIRECTIONS. FOR COTTON TREATED FOR MARKET YEAR 2024, EACH ACCELERON® SEED APPLIED SOLUTIONS OFFERING is a combination of separate individually registered products containing the active ingredients: BASIC Offering: fluoxastrobin, prothioconazole, metalaxyl, myclobutanil, and penflufen. STANDARD Offering: fluoxastrobin, prothioconazole, metalaxyl, myclobutanil, penflufen, and imidacloprid. ELITE plus Copeo® Offering: fluoxastrobin, prothioconazole, metalaxyl, myclobutanil, penflufen, imidacloprid, and fluropyram.
FOR COTTON TREATED FOR MARKET YEAR 2022 OR PRIOR, EACH ACCELERON® SEED APPLIED SOLUTIONS OFFERING is a combination of separate individually registered products containing the active ingredients: BASIC Offering: fluxapyroxad, pyraclostrobin, metalaxyl, and myclobutanil. STANDARD Offering: fluxapyroxad, pyraclostrobin, metalaxyl, myclobutanil, and imidacloprid. ELITE plus Poncho®/VOTiVO® Offering: fluxapyroxad, pyraclostrobin, metalaxyl, myclobutanil, imidacloprid, clothianidin, and Bacillus Firmus I-1582.
Please review each seed tag to determine active ingredients in the product offering on the seed. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Not all products are approved in all states.
ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW PESTICIDE LABEL DIRECTIONS. FOR SOYBEANS SEED TREATMENT PRODUCTS APPLIED DOWNSTREAM, EACH ACCELERON® SEED APPLIED SOLUTIONS OFFERING is a combination of separate individually registered products containing the active ingredients: BASIC Offering: metalaxyl, penflufen and prothioconazole. STANDARD Offering: metalaxyl, penflufen, prothioconazol and imidacloprid. FOR UPSTREAM TREATED SOYBEANS, EACH ACCELERON® SEED APPLIED SOLUTIONS OFFERINGis a combination of separate individually registered products containing the active ingredients: BASIC Offering: metalaxyl, fluxapyroxad, and pyraclostrobin. STANDARD Offering: metalaxyl, fluxapyroxad, pyraclostrobin and imidacloprid. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Not all products are approved in all states.
ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW PESTICIDE LABEL DIRECTIONS. FOR CORN, EACH ACCELERON® SEED APPLIED SOLUTIONS OFFERING is a combination of separate individually registered products containing the active ingredients: BASIC plus Poncho®/VOTiVO® Offering for corn: metalaxyl, ethaboxam, prothioconazole, fluoxastrobin, clothianidin, Bacillus firmus I-1582. ELITE plus Poncho®/VOTiVO® Offering for corn: metalaxyl, ethaboxam, clothianidin, and Bacillus firmus I-1582; prothioconazole and fluoxastrobin at rates that suppress additional diseases. BASIC Offering for corn: metalaxyl, prothioconazole, fluoxastrobin, ethaboxam, and clothianidin. ELITE Offering for corn: metalaxyl, ethaboxam, and clothianidin; and prothioconazole and fluoxastrobin at rates that suppress additional diseases. BioRise® Corn Offering is included seamlessly across offerings on all class of 2017 and newer products. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Not all products are approved in all states.
Performance may vary, from location to location and from year to year, as local growing, soil and weather conditions may vary. Growers should evaluate data from multiple locations and years whenever possible and should consider the impacts of these conditions on the grower’s fields.
The Bayer Carbon Program described in this material is subject to the current version of the Bayer Carbon-Smart Practices Master Agreement. The information is to aid in the understanding of the Bayer Carbon Program and does not change or modify the Bayer Carbon-Smart Practices Master Agreement in any way.
The RRXtend Spray App provides forecasts for locations within the contiguous United States. Do not use this app for forecasts outside the contiguous United States. Forecasts are for planning purposes only and are not a substitute for checking actual weather conditions at your location at the time of application and comply with the product label and other legal requirements.
B.t. products may not yet be registered in all states. Check with your seed brand representative for the registration status in your state.
Refuge seed may not always contain the DroughtGard® trait. Adament™ 50 WG Fungicide is only registered in California. Roundup Technology® includes glyphosate-based herbicide technologies.
IMPORTANT IRM INFORMATION: Certain products are sold as RIB Complete® corn blend products, and do not require the planting of a structured refuge except in the Cotton-Growing Area where corn earworm is a significant pest. Products sold without refuge in the bag (non-RIB Complete) require the planting of a structured refuge. See the IRM/Grower Guide for additional information. Always read and follow IRM requirements.
ONLY USE FORMULATIONS THAT ARE SPECIFICALLY LABELED FOR SUCH USES AND APPROVED FOR SUCH USE IN THE STATE OF APPLICATION. Contact the U.S. EPA and your state pesticide regulatory agency with any questions about the approval status of dicamba herbicide products for in-crop use with products with XtendFlex® Technology.
ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW PESTICIDE LABEL DIRECTIONS. It is a violation of federal and state law to use any pesticide product other than in accordance with its labeling. NOT ALL formulations of dicamba or glyphosate are approved for in-crop use with Roundup Ready 2 Xtend® soybeans. NOT ALL formulations of dicamba, glyphosate or glufosinate are approved for in-crop use with products with XtendFlex® Technology.
Roundup Ready® Technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate. Roundup Ready® 2 Technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate. LibertyLink® Technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glufosinate. Roundup Ready® Flex Technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate. Roundup Ready technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate, an active ingredient in Roundup® brand agricultural herbicides. Roundup Ready 2 Xtend® soybeans contain genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate and dicamba. Products with XtendFlex® Technology contains genes that confer tolerance to glyphosate, glufosinate and dicamba. Plants that are not tolerant to glyphosate, dicamba, and/or glufosinate may be damaged or killed if exposed to those herbicides. Contact your seed brand dealer or refer to the Bayer Technology Use Guide for recommended weed control programs.
Insect control technology provided by Vip3A is utilized under license from Syngenta Crop Protection AG. Movento® MPC Insecticide is only registered for use in Florida, Georgia and Alabama. Aeris®, Balance® Flexx, Baythroid® XL, Corvus®, Degree Xtra®, Harness® Xtra 5.6L Herbicide, Harness® Xtra Herbicide, Huskie® Complete, Leverage® 360, and TriVolt™ are restricted use pesticides. Not all products are registered for use in all states and may be subject to use restrictions. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Check with your local dealer or representative for the product registration status in your state. Fortenza Advanced™ is an on-seed application of Fortenza® and Rascendo® seed treatments. Agrisure Viptera®, Fortenza Advanced™, Fortenza® and Rascendo® are trademarks of Syngenta Group Company. Tank mixtures: The applicable labeling for each product must be in the possession of the user at the time of application. Follow applicable use instructions, including application rates, precautions and restrictions of each product used in the tank mixture. Not all tank mix product formulations have been tested for compatibility or performance other than specifically listed by brand name. Always predetermine the compatibility of tank mixtures by mixing small proportional quantities in advance. Degree® is a registered trademark of Monsanto Technology LLC. Channel®, Channel® and the Arrow Design® and Seedsmanship At Work® are registered trademarks of Channel Bio, LLC. Services and products offered by Climate LLC are subject to the customer agreeing to our Terms of Service. Our services provide estimates or recommendations based on models. These do not guarantee results. Consult with your agronomist, commodity broker, or other industry professional before making financial, farming, or risk management decisions. More information at www.climate.com/legal/disclaimer. FieldView™ is a trademark of Climate LLC. Herculex® is a registered trademark of Dow AgroSciences LLC. Clearfield®, Copeo®, ILeVO®, LibertyLink logo® , LibertyLink®, Poncho®, Poncho®/Votivo® and Votivo® are trademarks of BASF Corporation. Respect the Refuge and Corn Design® and Respect the Refuge® are registered trademarks of National Corn Growers Association. Some of the product(s) discussed herein are restricted use pesticide(s) and may not be registered in all states. The distribution, sale, or use of an unregistered pesticide is a violation of federal and/or state law and is strictly prohibited. Check with your local dealer or product representative for the product registration status in your state. Absolute®, Acceleron®, Adament™, Admire®, Aeris®, Aliette®, Alion®, Allegiance®, Asgrow and the A Design®, Asgrow®, Autumn™, Axiom®, Balance®, Bayer, Bayer Cross, Baythroid®, BioRise®, Bollgard II®, Bollgard®, BUTEO™ start, Capreno®, ConnectIN™, Corn States Triangle Design®, Corvus®, Degree Xtra®, DEKALB and Design®, DEKALB®, Delaro®, Deltapine Select™, Deltapine®, DiFlexx®, Disease Shield®, DroughtGard®, DryTough™, Emesto®, Evergol®, EverGol®, FarmFlex®, Finish®, Flint®, Fontanelle Hybrids and Design®, Fontanelle Hybrids®, Gaucho®, Gem®, Ginstar®, Gold Country Seed®, Ground Breakers®, H Hubner and Design™, Harness®, Hubner Seed & Design®, Hubner Seed Your Trustworthy Seed Resource & Design®, Hubner Seed™, Huskie®, Jung Seed Genetics & Design®, Jung Seed Genetics™, Kruger Seeds™, Laudis® , Leaf Triangle Design®, Leverage®, Lewis Hybrids and Design®, Lewis Hybrids™ , Lewis Premium Grains & Design®, Luna Experience®, Luna Privilege®, Luna Sensation®, Luna Tranquility®, Luna® Flex, Luna® Pro Fungicide, Luxxur®, MILK MAXX SILAGE RESEARCH and Design®, Minuet™, Movento®, Movento® HL, Nortron®, Oberon®, Olympus®, Poncho®, Preceon™, Proline®, Propulse®, Prosaro®, Prosper®, Provost®, Raxil®, REA Hybrids and Design™, Rea Hybrids™ , Respect the Refuge and Cotton Design®, RIB Complete and Design®, RIB Complete®, Ricestar®, Rimfire®, Roundup PowerMAX®, Roundup Ready 2 Technology and Design®, Roundup Ready 2 Xtend®, Roundup Ready 2 Yield®, Roundup Ready®, Roundup Technology®, Roundup WeatherMAX and Design®, Roundup WeatherMAX®, Roundup®, RT 3 Powered by Roundup Technology and Design®, RT 3®, Scala®, Serenade®, Serenade® SOIL fungicide, SilageSmart & Design®, SilageSmart®, Sivanto®, SmartStax®, Specialty and Design®, Specialty Hybrids™, SR and Design®, Stance®, Stewart and Design™, Stewart Seeds™, Stone Seed & Design™, Stone Seed™, Stratego®, ThryvOn™, Trecepta®, Trilex®, TripleFLEX®, TriVolt™, TruFlex™, VaporGrip®, Varro®, Velum®, Vistive®, VT Double PRO®, VT Triple PRO®, VT4PRO™, VT4PRO™ , Warrant®, WestBred and Design®, WestBred®, Wolverine®, XtendFlex®, XtendiMax® and YieldGard VT PRO® are trademarks of Bayer Group. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. For additional product information call toll-free 1-866-99-BAYER (1-866-992-2937) or visit our website at www.BayerCropScience.us. Bayer CropScience LP, 800 North Lindbergh Boulevard, St. Louis, MO 63167. ©2024 Bayer Group. All rights reserved.







©2024 Bayer Group. All rights reserved.