3 MIN READ
Holcus Leaf Spot in Corn
June 29, 2016
- Holcus leaf spot is a bacterial disease that generally enters corn plants through wounds caused by thunderstorms, high winds, or hail.
- It is important to carefully identify Holcus leaf spot as symptoms may also resemble other fungal diseases or herbicide injury.
- Although plants may exhibit symptoms, yield potential is rarely affected.
Background
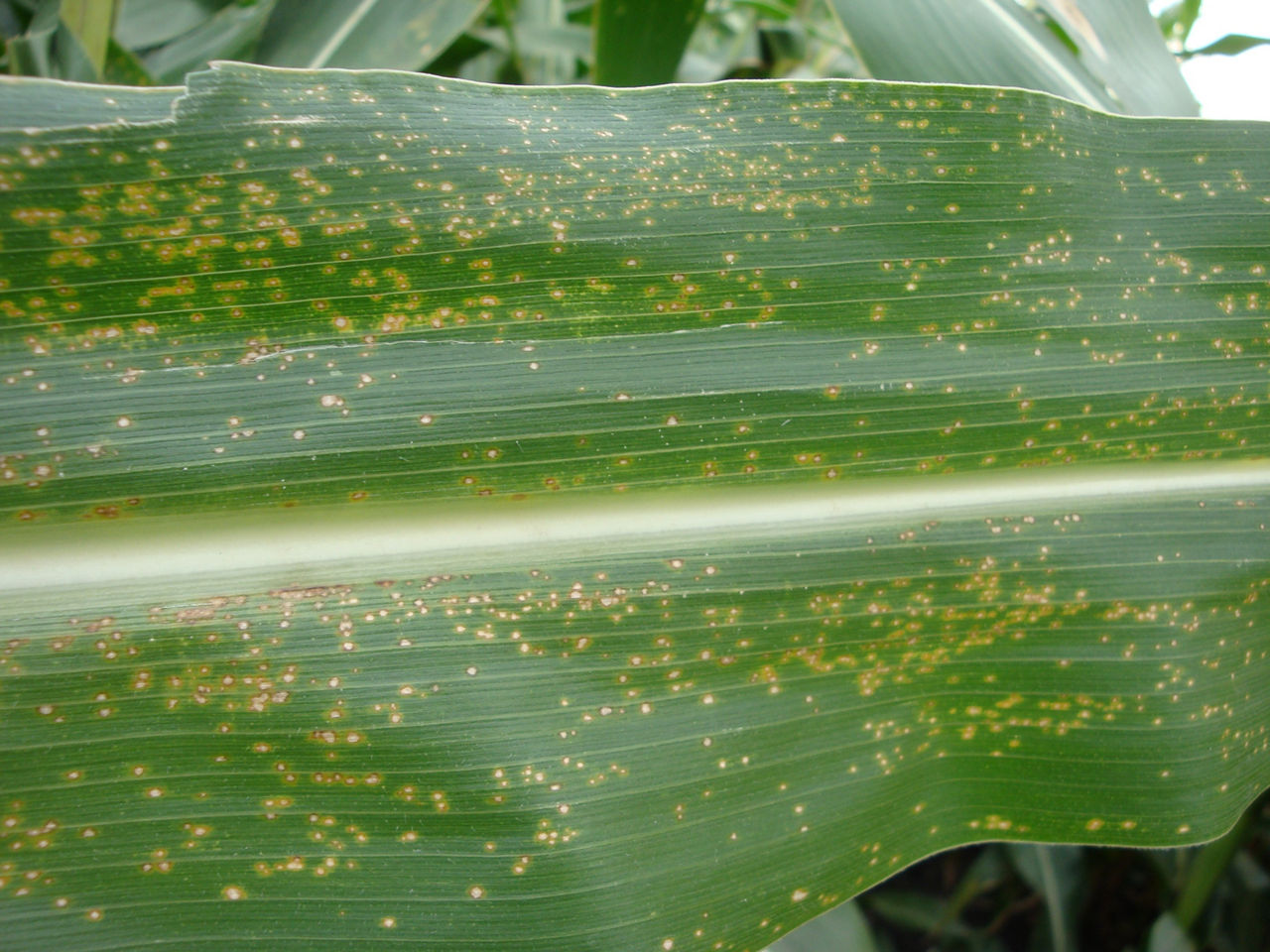
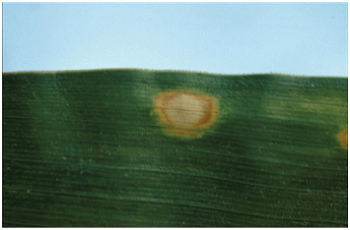
Holcus leaf spot is a corn pathogen caused by the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. This pathogen overwinters in a variety of hosts that include both monocot and dicot species. Incidence of the disease typically occurs earlier in the growing season after heavy winds or thunderstorms.1 Hail and damage from blowing soil can create plant wounds that enable disease transmission.2 Plant injury is not required for disease transmission, as Holcus leaf spot may also enter natural plant openings like stomata (transpiration openings).3 Extended wet weather and warm temperatures can also increase the appearance of symptoms, but new leaves typically are not affected.1,2
Identification
Crop Impact
Holcus leaf spot is generally superficial, and does not negatively impact corn yield potential. Management of weedy hosts and tillage may help reduce overwintering of the pathogen in crop residue, but only when it is practical to do so.3 There are no in-season management options for Holcus leaf spot. It is important to carefully distinguish between Holcus leaf spot, which does not require treatment, and a possible fungal disease which may benefit from a fungicide application.
Sources
1 Crop Diseases Team. Holcus spot. University of Minnesota Extension. http://www.extension.umn.edu/.
2 Robertson, A. 2004 Holcus leaf spot being found on corn. Iowa State University. IC-492(14). http://www.ipm.iastate.edu/.
3 Jackson, T. and Timmerman, A. 2011. Foliar diseases of corn developing across Nebraska. University of Nebraska-Lincoln. CropWatch. http://cropwatch.unl.edu/. Web sources verified 06/15/16. 160614094527