3 MIN READ
Iron Deficiency Chlorosis Tolerance in Soybean Products Grown on Calcareous Soils
January 30, 2022
Trial Objective
Soybean growers gauge chlorosis response of soybean products to calcareous soils and growing conditions. Soybean product selection is one of the most efficient management tools to combat iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC) in soybean production.
To address the need for updated information on soybean product responses, this research evaluated nine commercially available soybean products for tolerance to IDC.
The objective of this study was to determine local soybean products with greater tolerance to IDC and gain perspective of product IDC ratings for the Central Plains region.
Site Details
| Location | Assaria, KS |
| Soil Type | New Cambridge silty clay |
| Previous Crop | Corn |
| Tillage Type | Conventional |
| Planting Date | 6/21/21 |
| Harvest Date | 10/20/21 |
| Potential Yield (bu/acre) | 80 |
| Seeding Rate (seeds/acre) | 150,000 |
- Trial location was identified based on occurrence of IDC in previous soybean crops as observed by the farmer cooperator. The previous crop was double-crop corn.
- Weeds were controlled uniformly across the study.
- Irrigation was estimated as 8 inches for the crop growing season.
- Soil pH ranged from 8 to 8.2.
- The study was a strip trial design evaluating 9 soybean products.
- Plots consisting of 6 rows and soybeans were planted into 30-inch rows at a depth of 1.5 inches.
- A 9-point scale was employed to score the severity of IDC symptoms, with a score of
- 1 = Excellent - green no yellowing
- 2 = Very Strong - little to no yellowing
- 3 = Strong - minimal yellowing
- 4 = Average - mild yellowing
- 5 = Above Average - moderate interveinal chlorosis
- 6 = Below Average - pronounced interveinal chlorosis
- 7 = Weak - severe interveinal chlorosis
- 8 = Very Weak - predominantly yellow
- 9 = Poor - dead meristems or plants
Table 1. Soybean grain moisture, test weight, yield, and IDC ratings according to maturity group.
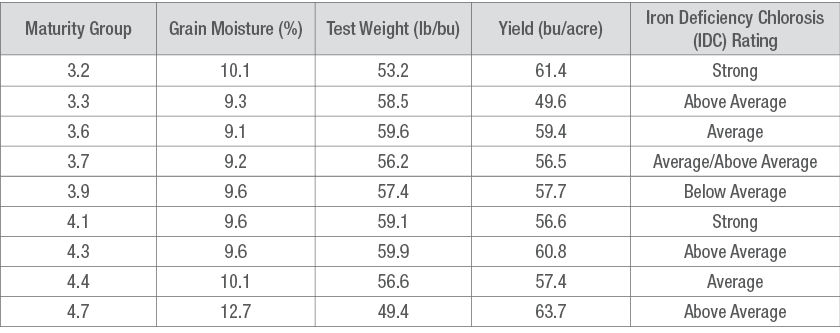
- All soybean products tested showed IDC tolerance at some level. Yield differences between soybean products is due to relative maturity as well as IDC rating.
- Overall, soybean yielded well despite the extended periods of drought in the area during the 2021 growing season.
- Seasonal rainfall accumulation was 27.6 inches, approximately 4 inches less than the 10-year average.
- Growers applied irrigation more often this year as compared to the last 3 years in this field.
Key Learnings
- All the soybean products in this study exhibited some level of tolerance to IDC. The difference in one product to the next is a result of a complex interaction between plant physiological response to soil characteristics, topography, weather, and irrigation practices. Screening soybean products for iron-deficiency chlorosis is critical for farmers with fields with a history of Fe chlorosis.
- Reduced plant growth due to any IDC symptoms can have a negative effect on yield potential. Significant yield reductions have been attributed to IDC throughout the north central United States. Planting soybean products with higher IDC tolerance is an effective technique to protect against yield losses related to IDC.
- Correcting IDC can be very difficult, and the most important management consideration is to identify products with greater IDC tolerance to minimize plant stress. Selecting the best soybean product for fields with a history of IDC decreases plant death rates and increases the likelihood of plants to recover from iron-deficiency chlorosis.
1006_R2_21
Seed Brands & Traits
Crop Protection
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.
©2024 Bayer Group. All rights reserved.