The Response of Deltapine® Brand Cotton Varieties to Plant Growth Regulator Applications
February 3, 2025
Click on a tab below to see data collected each year for this study
TRIAL OBJECTIVE
- This study was conducted to evaluate the yield characteristics and plant growth regulator (PGR) response of Deltapine® brand cotton varieties, including two new Class of ‘25 varieties.
- Knowing the growth characteristics of cotton varieties and their relative sensitivity to PGR applications is important for determining how to manage different cotton varieties. These studies at the Bayer Crop Science Learning Center at Scott, MS help expand information about available products, including those with ThryvOn® Technology.
- This study intends to provide basic considerations for how aggressively new cotton varieties should be managed relative to each other.
- Information on proper growth management for Deltapine® brand cotton varieties can help optimize performance potential.
RESEARCH SITE DETAILS
- There were nine Deltapine® brand cotton varieties planted in this trial:
- DP 2211 B3TXF
- DP 2414 B3TXF
- DP 2317 B3TXF
- DP 2127 B3XF
- DP 2537 B3TXF (Class of ’25)
- DP 2522NR B3TXF (Class of ’25)
- DP 2328 B3TXF
- DP 2333 B3XF
- DP 2038 B3XF
- Plant growth regulator treatments included:
- Untreated control (UTC)
- Passive (PASS) PGR management with 4.2% mepiquat applied at the following timing:
- 7/3/2024: 12 fl oz/acre
- 7/17/2024: 16 fl oz/acre
- 8/1/2024: 16 fl oz/acre
- Aggressive (AGG) PGR management with 4.2% mepiquat applied at the following timing:
- 6/21/2024: 16 fl oz/acre
- 7/3/2024: 16 fl oz/acre
- 7/17/2024: 16 fl oz/acre
- The trial was planted into a field with 140 lb nitrogen (N) surface applied as 30-0-0-2.5 prior to layby.
- Each treatment was planted as a 6-row strip trial with 0.17 to 0.21 acres per plot.
- All field work, tillage, and herbicide applications were per local standards.
- Data collected for this trial included:
- End of season plant heights, collected from 10 plants per plot
- Yield, whole plot machine harvested
- Representative site turn outs (Heaven Cut variety evaluation) were used for lint yield estimations
This trial included five of the NPE (New Product Evaluator) varieties tested during 2024. Three of those products were not advanced, so they were removed from the field part of the analysis. The two advanced products were renamed and included in the analysis.
UNDERSTANDING THE RESULTS
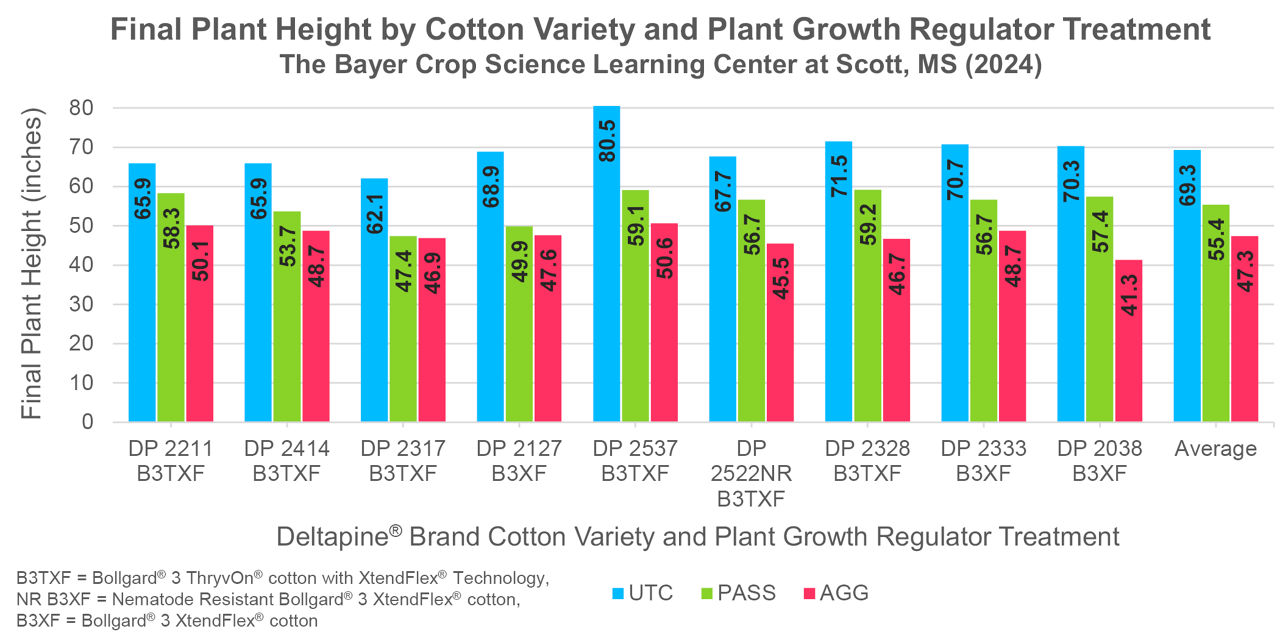
Plant Heights
- Height reductions across this study were in the range that would be expected. Notable results include:
- End of Season Heights (Figure 1)
- UTC
- Ranged from 62.1 to 80.5 inches tall
- UTC Average height: 69.3 inches
- PASS
- Ranged from 47.4 to 59.2 inches tall
- UTC Average Height: 55.4 inches
- Average height reduction vs UTC: 13.9 inches
- AGG
- Ranged from 41.3 to 50.6 inches tall
- Average: 47.3 inches
- Average height reduction vs UTC: 21.9 inches
- UTC
- End of Season Heights (Figure 1)
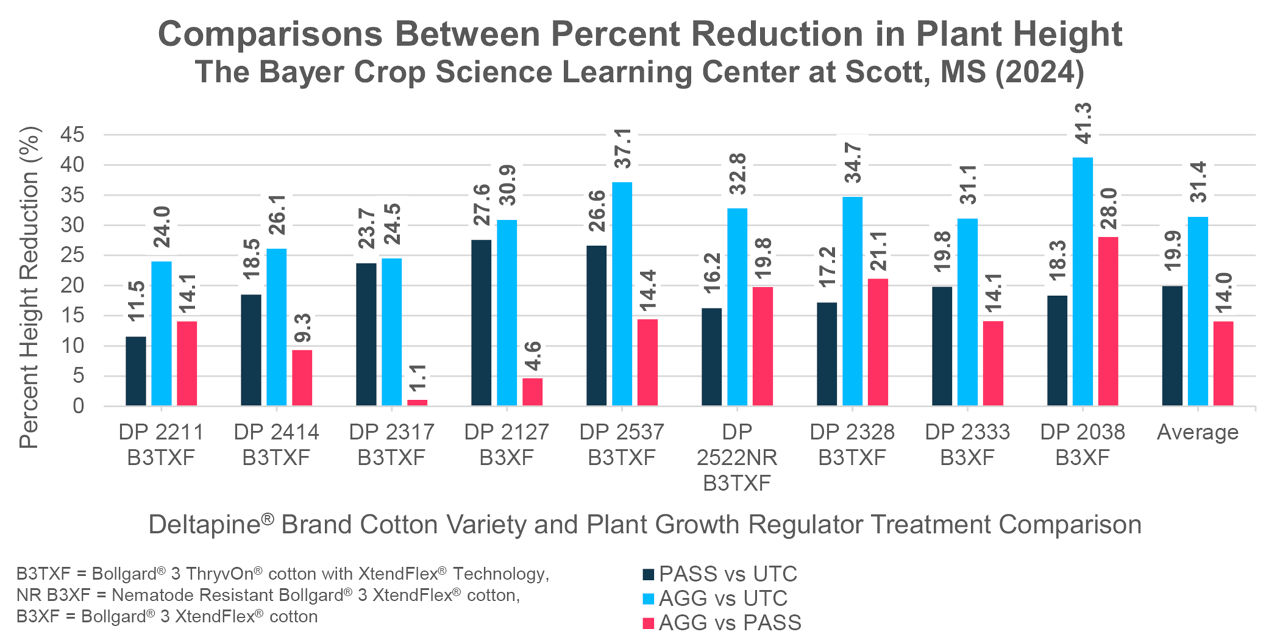
Percent Height Reduction
- PASS vs UTC
- Average reduction: 19.9%
- Ranged from 11.5 to 27.6%
- AGG vs UTC
- Average reduction: 31.4%
- Ranged from 24.0 to 41.2%
- AGG vs PASS
- Average reduction: 14.1%
- Ranged from 1.1 to 28.1%
- This comparison is a new inclusion and has been included as an indicator of the relative value of PGR use across a group of cotton varieties. It basically defines the “extra” response from being more aggressive in rate/timing with PGR applications.
- The varieties can be considered as part of one of three groups. Conclusions by group include:
- Group One, Low Growth Potential:
- Examples: DP 2211 B3TXF, DP 2414 B3TXF, DP 2317 B3TXF.
- INTERPRETATION: Data indicate these varieties to be less responsive to PGRs and in this study, they were. This is not a result of being overly growthy, but rather because they are very determinate and typically accumulate a fruit load that helps provide mid-season growth control. These varieties are also likely more sensitive to stressed growing conditions.
- Group One, Low Growth Potential:
- Group Two, Medium Growth Potential:
- Examples: DP 2522NR B3TXF, DP 2328 B3TXF, DP 2038 B3XF.
- INTERPRETATION: Data indicate these varieties show moderate response to PGRs and this was also observed in this study. These varieties can fruit weakly in the lower crop and need PGR intervention to settle back into a stable fruiting pattern. Conditions may lead them to fruit either well or weakly in the bottom crop, thereby emphasizing the need for scouting and intervention as needed.
- Group Three, High Growth Potential:
- Examples: DP 2127 B3XF, DP 2537 B3TXF, DP 2333 B3XF.
- INTERPRETATION: Data indicate these varieties show the lowest response to PGR application. This can be due to a combination of several factors, including very aggressive early season growth, and a prioritization of vegetative growth over reproductive growth during the season leading to reduced fruiting and increased fruit shed. These varieties are typically less determinate or more indeterminate, and more stress tolerant. They are the most difficult to control in strong growth conditions or during times of reduced fruit load due to insect damage, weather events, etc. These are the varieties where AWARENESS is critical for success.
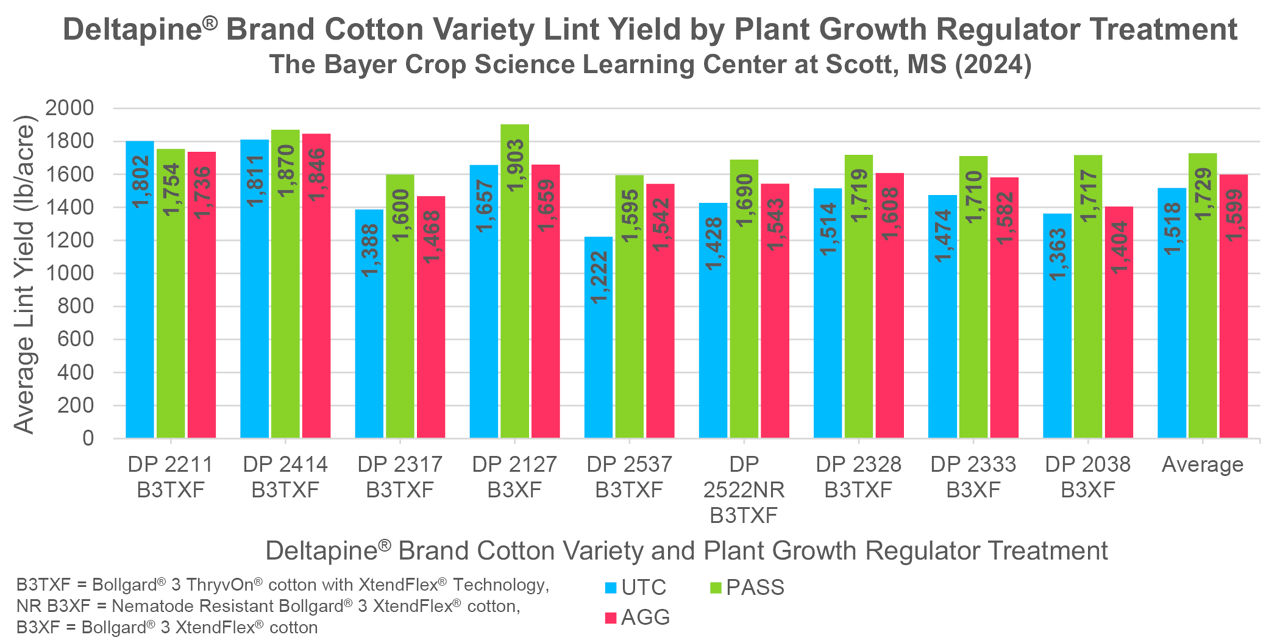
- Yield Results
- UTC average lint yields = 1,518 lb/acre
- Passively managed (PASS) average lint yields = 1,729 lb/acre
- Aggressively managed (AGG) average lint yields = 1,599 lb/acre
- In this study, there was a 211 lb/acre average lint yield increase across all varieties from the PASS applications compared to the UTC.
- There was a 130 lb/acre average lint yield increase across all varieties from the AGG applications compared to the UTC.
- Most of the varieties tested demonstrated the highest yield potential under the passive PGR treatment. This is a typical result and not the primary goal of this trial. The primary goal is to measure the relative growth control response in height from similar rates and timings of PGR use.
- Most varieties demonstrated a yield increase between 200 and 350 lb/acre in response to the passive treatment compared to the UTC.
- DP 2537 B3TXF stood out in this trial as it had the largest yield increase for both application regimes. It was also the tallest variety in the UTC plot at 80+ inches. Both factors indicate the need for relatively aggressive growth control when growing this variety. DP 2537 B3TXF typically exhibits aggressive growth early and the need for timely and proper PGR intervention is essential for optimizing its performance.
- While DP 2522NR B3TXF typically has a moderate PGR response, the variety is reniform nematode resistant. Reduction in nematode root feeding could lead to aggressive early season development (and the inherent fruiting shifts that occur in such circumstances) in the variety. This is a critical point of awareness for this product.
KEY LEARNINGS
- The tested varieties showed a range of sensitivity to PGR use that would be expected, but each product is different and must be viewed that way.
- Varieties that appeared to be very sensitive to PGR applications and/or not extremely aggressive in growth habit through the season will likely require less aggressive management strategies and should probably be planted on stronger production systems.
- DP 2333 B3XF and DP 2537 B3TXF appear to be less growth-responsive to PGR management and can be highly yield-responsive to intensive PGR management. For this reason, growers should carefully plan and implement appropriate PGR strategies when planting these varieties.
- When planted into reniform infested fields, DP 2522 B3TXF should be closely monitored for needed PGR interventions from early to mid-season.
- Each field, farm, and scenario should be carefully evaluated before implementing any PGR strategy. This should include consideration of established plant population, fertility, rotational crops, current growth rate, and varietal response to PGR use.
- Please contact your local Deltapine® brand representative for more information.
1414_340645
You may also like...
Here are some articles that may also be of interest to you