4 MIN READ
Managing Corn Rootworm
July 30, 2022
ROOTWORM RISKS ARE LOWER… DO I STILL NEED PROTECTION?
A survey conducted in Illinois earlier this summer found lower numbers of corn rootworm beetles than usual, so risks were projected to be lower for 2016. However, later this season field reps are reporting observations of greater than expected numbers of beetles in Illinois. Dr. Michael Gray explains in this article that this enforces the importance of taking proper precautions. Follow best management practices - like planting corn with multiple modes of action against rootworm (such as SmartStax® corn), and scouting your fields early and often. Do not assume your risks are low until you can confirm it in each of your fields.
SMALL ENEMY. BIG PROBLEM.
Corn rootworm damage causes over $1 billion in lost revenue annually. Corn rootworm larvae are often one fourth to half an inch long and they live underground.
So how can you tell if they're in your field?
ASSESS YOUR RISK
- Scout to identify current pest pressure in your fields
- Consult your seed representative to discuss pressure across your fields
ROOTS

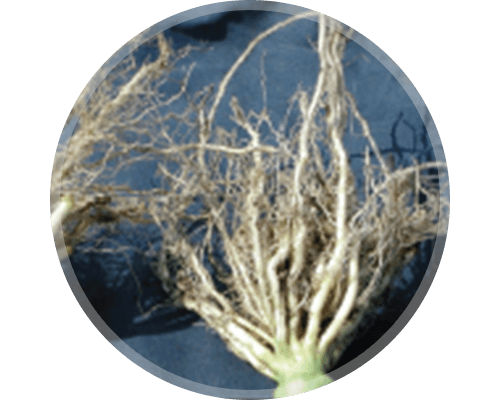
Current Damage Assessment: Root Digs
Dig Timing: mid-June - mid-July
Dig a series of corn root balls (one foot in diameter), shake off the soil, and wash roots.
Root damage due to CRW larval feeding consists of brown feeding scars often along the side of the roots, tunneling inside the larger roots, and root pruning with the roots eaten back toward the base of the stalk.
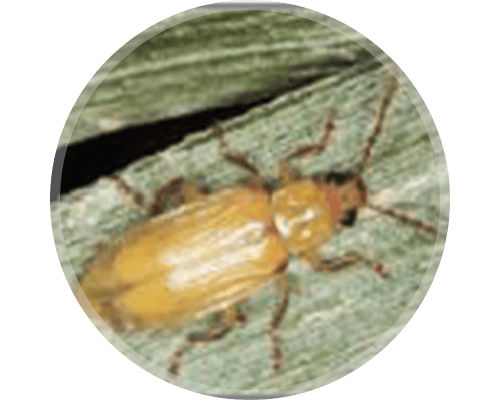
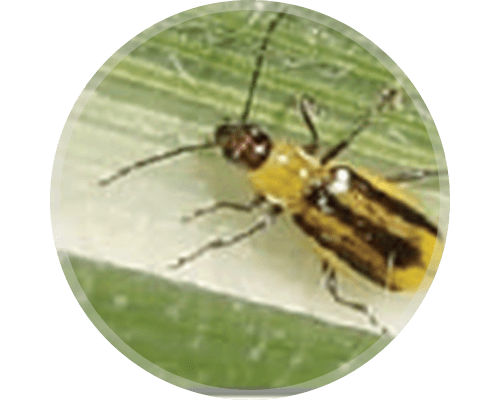
INSECTS
Infestation Assessment: Scout for corn rootworm beetles
Scouting Timing: July-August
CRW beetle counts are a key component in assessing the potential number of eggs that may be laid in a field. Most often, the CRW beetle populations within a field hatched in that same field.
Scouting is a tool to better understand the current rootworm pressure and should serve as a primary source of information to help to make an informed decision for current and future CRW management. Reducing beetle numbers before they lay eggs by using a foliar insecticide application can help to reduce corn rootworm pressure the following year.


Production Practices that can result in increased CRW Populations
- Planting continuous corn
- Late-planted corn fields relative to others in the area
- Planting late maturity hybrids such as those used for silage
Develop a Strategy
Product selection is the first step in developing a strategy for your field. If corn rootworm is present in your field, the following recommendations should be considered:
In-Season Management
- Conduct ongoing scouting to monitor population levels.
- Manage adult corn rootworm beetle populations based on economic thresholds.
- Consult your seed representative to discuss pressure across your fields
